Body Implants
Body Implant Surgery in Carmel, IN
Barry L. Eppley, MD, DMD has the most extensive body implant experience of any plastic surgeon in creating increased muscular volume from the chest down to the calves.
MOST BODY IMPLANTS ARE MUSCLE ENHANCERS
Increasing the size of certain body muscles, or muscular enhancement, is the objective of most body implants. Other than breast implants (which is not a muscular enhancer), the most commonly historically used body implants were the buttock, calf and pectoral implants. While once viewed as unusual or rare procedures, body implant surgery today is fairly common as implant materials and surgical techniques have improved. This has also lead to new innovative implants and areas for augmentation such as arm (biceps and triceps), shoulders (deltoid and trapezius), thighs and hip implants. While fat injection augmentation has a valuable role in the enhancement of certain body areas, synthetic implants offer a permanent and assured solution to body augmentation that has the trade-off of an implanted synthetic material and a longer recovery.
 Muscle implants are used to surgically build-out or augment an underdeveloped or deficient area of muscle in the body. These muscle ‘weaknesses’ can be caused by a congenital defect, a traumatic injury, or more commonly, an aesthetic desire for improvement in one’s self-esteem. Aesthetic desires for body implants come from an inability to build up the muscle adequately through exercise, and/or a disproportion to the rest of the body. There are also recent fashion and cultural influences that have increased the desires for larger chests and buttocks. Congenital defects that lead some patients to receive body implants can include club foot, chest wall deformities from Pectus and Poland’s syndrome (pectoral implants) and Sprengel’s deformity (deltoid implants).
Muscle implants are used to surgically build-out or augment an underdeveloped or deficient area of muscle in the body. These muscle ‘weaknesses’ can be caused by a congenital defect, a traumatic injury, or more commonly, an aesthetic desire for improvement in one’s self-esteem. Aesthetic desires for body implants come from an inability to build up the muscle adequately through exercise, and/or a disproportion to the rest of the body. There are also recent fashion and cultural influences that have increased the desires for larger chests and buttocks. Congenital defects that lead some patients to receive body implants can include club foot, chest wall deformities from Pectus and Poland’s syndrome (pectoral implants) and Sprengel’s deformity (deltoid implants).
Body implants, unlike breast implants, are composed of a solid but very soft silicone elastomer material. Since they are not fluid or gel-filled, there is no chance that they will ever rupture, degrade or need to replaced due to a material-related problem. Body implants surgery is perfectly safe, but requires a surgeon skilled in using these materials who has the knowledge and experience to operate in a variety of anatomical locations throughout the body.
BUTTOCK IMPLANTS
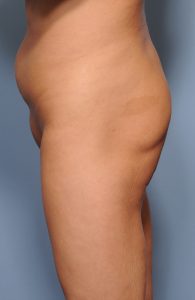
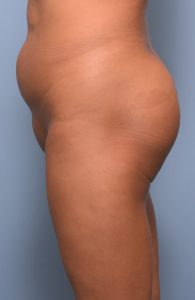
 Offering a permanent solution to aesthetic buttock augmentation, implants are either the alternative to fat injections when there is not enough fat to harvest or the next step when fat injections have failed to produce desired results.
Offering a permanent solution to aesthetic buttock augmentation, implants are either the alternative to fat injections when there is not enough fat to harvest or the next step when fat injections have failed to produce desired results.
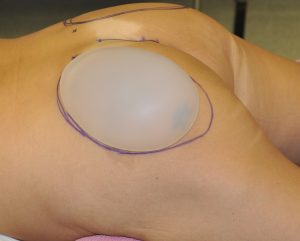
 Buttock implants are inserted through an intergluteal incision and can be placed either into (intramuscular) or on top of the gluteus maximus muscle but underneath the overlying fascia. The intramuscular location is the preferred pocket to reduce the risk of potential complications as opposed to on top of it. But such intramuscular placement poses limitations in the size of the implant which can be placed which is its main drawback. The subfascial pocket provides the ability to have larger sizes but has a higher risk of fluid collections (seroma) and implant migration/displacement.
Buttock implants are inserted through an intergluteal incision and can be placed either into (intramuscular) or on top of the gluteus maximus muscle but underneath the overlying fascia. The intramuscular location is the preferred pocket to reduce the risk of potential complications as opposed to on top of it. But such intramuscular placement poses limitations in the size of the implant which can be placed which is its main drawback. The subfascial pocket provides the ability to have larger sizes but has a higher risk of fluid collections (seroma) and implant migration/displacement.
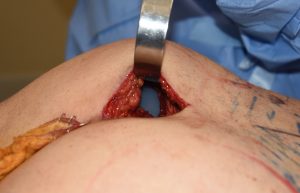
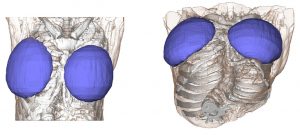
 Buttock implants are available in sizes up to 700ccs and in round and anatomic shapes. The majority of buttock implants patient receive implants in the 300 to 450cc range of a round shape. Most buttock implant results are not going to provide any associated hip augmentation effect of any significance.
Buttock implants are available in sizes up to 700ccs and in round and anatomic shapes. The majority of buttock implants patient receive implants in the 300 to 450cc range of a round shape. Most buttock implant results are not going to provide any associated hip augmentation effect of any significance.
Custom Buttock Implants Dr Barry Eppley IndianapolisThere are certain situations where they fabrication of a custom buttock implant may be needed. This is usually when one has existing buttock implants in place and a larger size is desired that is not commercially available. It may also be done to make unique designs that promote greater tissue adherence and limited forms of tissue ingrowth into the implant.
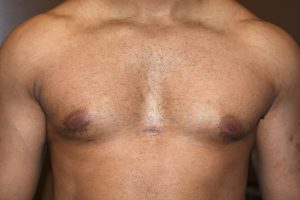
PECTORAL IMPLANTS
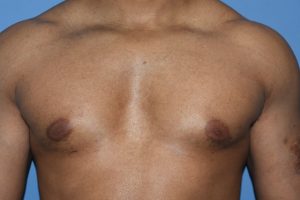
 While some may call pectorals implants the equivalent to female breast implants, there are some significant differences. Male chest enhancement by implants is done to increase the size and muscular definition of the pectoralis major muscle. As a result the implant must stay completely within the borders of the muscle. Pectoral implants, unlike breast implants, are made of solid soft silicone. As a result they will last a lifetime and will never degrade or need to be replaced.
While some may call pectorals implants the equivalent to female breast implants, there are some significant differences. Male chest enhancement by implants is done to increase the size and muscular definition of the pectoralis major muscle. As a result the implant must stay completely within the borders of the muscle. Pectoral implants, unlike breast implants, are made of solid soft silicone. As a result they will last a lifetime and will never degrade or need to be replaced.
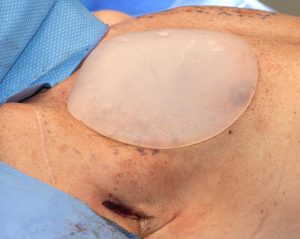
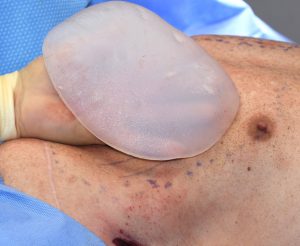 Pectoral implants are always placed under the pectorals major muscle but above the pectoralis minor muscle. They are best inserted through an incision placed high up in the armpit (transaxillary approach) for a more hidden scar location
Pectoral implants are always placed under the pectorals major muscle but above the pectoralis minor muscle. They are best inserted through an incision placed high up in the armpit (transaxillary approach) for a more hidden scar location
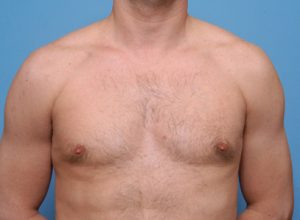
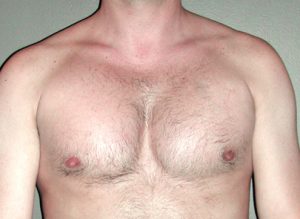 Pectoral implants are available in oval and more rectangular shapes with various thicknesses. (projection) Matching the pectoral implant to the patient’s muscular anatomy and their augmentation goals requires a lot of experience as, unlike breast implants, there are no volumetric sizers or exact formula as to how to make the optimal implant selection.
Pectoral implants are available in oval and more rectangular shapes with various thicknesses. (projection) Matching the pectoral implant to the patient’s muscular anatomy and their augmentation goals requires a lot of experience as, unlike breast implants, there are no volumetric sizers or exact formula as to how to make the optimal implant selection.
Pectoral Implant Funnel Insertion technique Dr Barry Eppley IndianapolisPectoral implants are placed through a high axillary incision to keep it hidden. How does a pectoral implant, which is much bigger than the incision, get through it into the implant pocket? A very good way to do so is with the use of the insertion funnel which is a technique borrowed that of breast implants.
ARM IMPLANTS (Biceps and Triceps)

 The top (bicep) and bottom (tricep) areas of the arm can be built up for those men who either can’t get enough muscle bulk by exercise alone or want to maintain a more muscular arm shape with less long-term exercise maintenance. Biceps and tricep implants look somewhat similar int appearance but the tricep implant is longer and has less central projection than a bicep implant. (similar to the actual muscle’s natural appearance)
The top (bicep) and bottom (tricep) areas of the arm can be built up for those men who either can’t get enough muscle bulk by exercise alone or want to maintain a more muscular arm shape with less long-term exercise maintenance. Biceps and tricep implants look somewhat similar int appearance but the tricep implant is longer and has less central projection than a bicep implant. (similar to the actual muscle’s natural appearance)
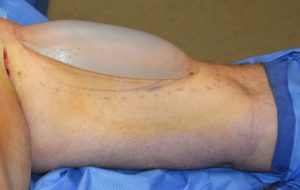
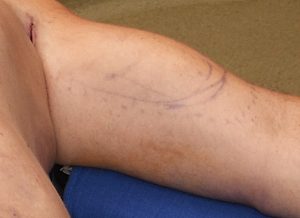 Bicep implants are primarily placed through a high incision in the armpit with the implant in the subfascial position on top of the muscle. The alternative approach is a medial arm incision where the implant is placed beneath the muscle on top of the bone.
Bicep implants are primarily placed through a high incision in the armpit with the implant in the subfascial position on top of the muscle. The alternative approach is a medial arm incision where the implant is placed beneath the muscle on top of the bone.
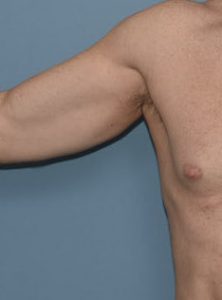
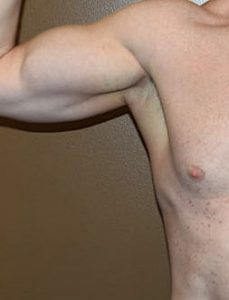 Tricep implants are inserted from an incision in the posterior axillary fold and is ideally best done from the prone position in surgery. It can be done in the supine position in surgery but is more challenging. Like the bicep implant it is placed on top of the muscle under the fascia. Most tricep implants are combined with bicep implants too give an overall more muscular upper arm appearance.
Tricep implants are inserted from an incision in the posterior axillary fold and is ideally best done from the prone position in surgery. It can be done in the supine position in surgery but is more challenging. Like the bicep implant it is placed on top of the muscle under the fascia. Most tricep implants are combined with bicep implants too give an overall more muscular upper arm appearance.
SHOULDER IMPLANTS (Deltoid and Trapezius)
 Deltoid implants are designed to widen the shoulders and/or create an enhanced muscle appearance. They are one of the three options in shoulder widening surgery. (fat grafting and clavicle lengthening being the other two) They can also be of benefit in loss of the deltoid muscle size from injury or a congenital Sprengel’s deformity. (scapular hypoplasia) Presently no true deltoid implants are commercially made and I use a custom implant design approach for them.
Deltoid implants are designed to widen the shoulders and/or create an enhanced muscle appearance. They are one of the three options in shoulder widening surgery. (fat grafting and clavicle lengthening being the other two) They can also be of benefit in loss of the deltoid muscle size from injury or a congenital Sprengel’s deformity. (scapular hypoplasia) Presently no true deltoid implants are commercially made and I use a custom implant design approach for them.
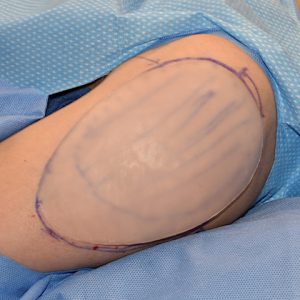
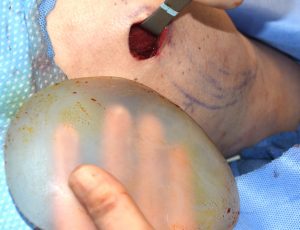 Deltoid implants are placed in the subfascial pocket over the muscle. The incisional approaches can be either from the posterior axillary fold or directly from above at the shoulder skin crease just to the side of the acromi0clavicular bony prominence. I have found that the direct approach coming from above allows the best implant positioning. Deltoid implants need to stay ‘high’ to have their maximal effect and low positioning is both aesthetically and sec0ndarily trying to repositi0n them undesirable.
Deltoid implants are placed in the subfascial pocket over the muscle. The incisional approaches can be either from the posterior axillary fold or directly from above at the shoulder skin crease just to the side of the acromi0clavicular bony prominence. I have found that the direct approach coming from above allows the best implant positioning. Deltoid implants need to stay ‘high’ to have their maximal effect and low positioning is both aesthetically and sec0ndarily trying to repositi0n them undesirable.
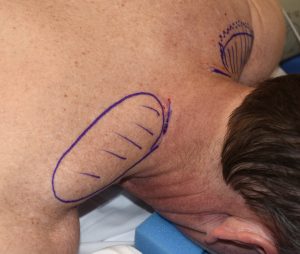 Trapezius implants provide enhancement to the upper border of the muscle so it appears more pronounced between the side of the neck and top of the shoulders. These are the smallest of all body muscle implants and are placed through small incisions at the base of the back of the neck.
Trapezius implants provide enhancement to the upper border of the muscle so it appears more pronounced between the side of the neck and top of the shoulders. These are the smallest of all body muscle implants and are placed through small incisions at the base of the back of the neck.
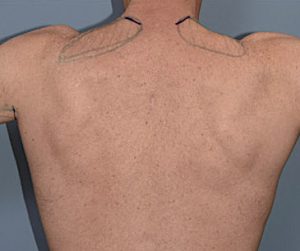
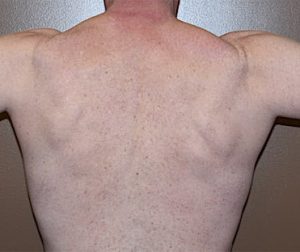 This is a difficult area of the upper back muscle to enlarge and it only takes a small implant placed along the upper edge of the muscle to make a visible difference.
This is a difficult area of the upper back muscle to enlarge and it only takes a small implant placed along the upper edge of the muscle to make a visible difference.
FOREARM IMPLANTS
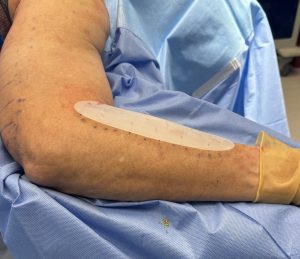
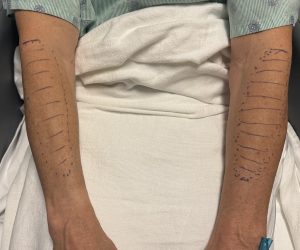
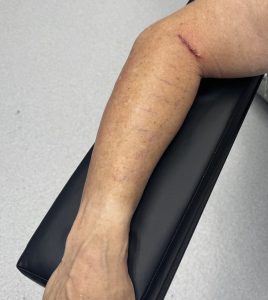
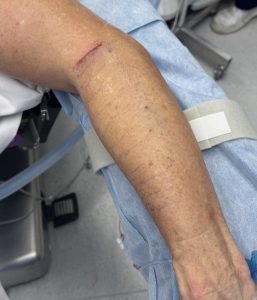 Augmentation of the upper arm is not limited to the muscles above the elbow. While the forearm has many more muscles than the upper arm (20 vs 4) they are such smaller and the options for augmentation of them are very limited. The one forearm muscle that has enough size to augment is the brachi0radialis, a fusiform-shaped muscle at the lateral forearm that has its biggest width by the cubital fossa. (elbow pit) Custom designed implants can be placed in the subfascial pocket to produce a more prominent muscle bulge or an overall bigger lateral forearm effect.
Augmentation of the upper arm is not limited to the muscles above the elbow. While the forearm has many more muscles than the upper arm (20 vs 4) they are such smaller and the options for augmentation of them are very limited. The one forearm muscle that has enough size to augment is the brachi0radialis, a fusiform-shaped muscle at the lateral forearm that has its biggest width by the cubital fossa. (elbow pit) Custom designed implants can be placed in the subfascial pocket to produce a more prominent muscle bulge or an overall bigger lateral forearm effect.
HIP IMPLANTS
For those women with perfectly straight hips (‘boy hips’) who want some curves or for those that desire more of an hourglass figure than they already have, hip augmentation cannot be successfully achieved with any form of exercise. Injection fat grafting is the preferred primary method if one has enough fat to harvest. Unlike fat injections into the buttocks, however, hip fat injections do not fare as well in terms of volume survival for reasons not yet known. But despite its poor success at hip augmentation persistence I would still advise that fat injections are attempted if one has adequate fat stores to do it. It may work for some people and, even if it doesn’t, it ‘prepares’ the hip augmentation site for implants by improving soft tissue quality.

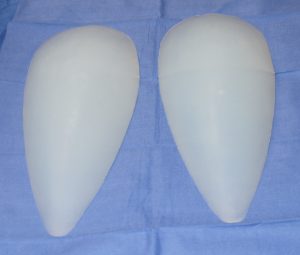
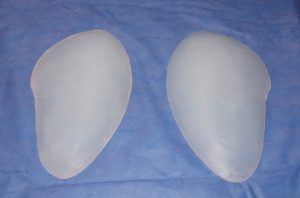
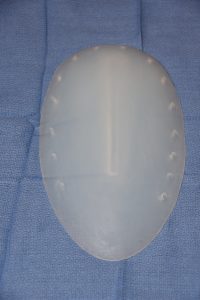 Currently there are no standard implants that are commercially available that are specifically made for the hips. There are some body implants for use in other areas that can be used as hip implants and that may work for some patients. But in general I prefer a custom hip implant design approach to better meet each patient’s anatomic and aesthetic needs. The hips are unique in that they do not have a natural shape that responds to augmentation well with circular or more cigar-shaped body implants like the buttocks or the extremities. They have a more complex shape that wraps around the hip area. While it does have a longer than wider shape it covers a broader surface area than one would think which is why it is a transitional area seen from the front of the thigh back to the buttocks. This anatomy combined with patient-specific aesthetic desires makes it hard to use other preformed body implants and have them turn out well.
Currently there are no standard implants that are commercially available that are specifically made for the hips. There are some body implants for use in other areas that can be used as hip implants and that may work for some patients. But in general I prefer a custom hip implant design approach to better meet each patient’s anatomic and aesthetic needs. The hips are unique in that they do not have a natural shape that responds to augmentation well with circular or more cigar-shaped body implants like the buttocks or the extremities. They have a more complex shape that wraps around the hip area. While it does have a longer than wider shape it covers a broader surface area than one would think which is why it is a transitional area seen from the front of the thigh back to the buttocks. This anatomy combined with patient-specific aesthetic desires makes it hard to use other preformed body implants and have them turn out well.
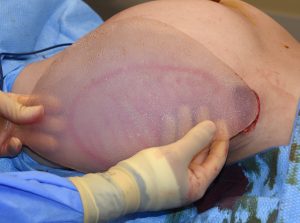 Hip implants are inserted from a superior approach using a small incision about at the level of the iliac crest. What makes hip implants unique is that to get the most desired shape result it has to be placed on top of the TFL fascia. While this works best from an aesthetic standpoint it also makes it highly prone to postoperative fluid collections (seroma) and possible implant edge reveal with significant hip flexion.
Hip implants are inserted from a superior approach using a small incision about at the level of the iliac crest. What makes hip implants unique is that to get the most desired shape result it has to be placed on top of the TFL fascia. While this works best from an aesthetic standpoint it also makes it highly prone to postoperative fluid collections (seroma) and possible implant edge reveal with significant hip flexion.
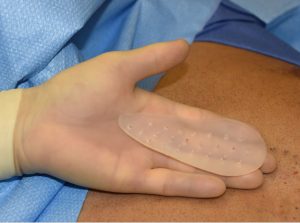
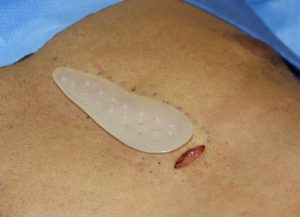
Custom Hip Implants and perfusion holes Dr Barry Eppley IndianapolisBesides the use of drains in the postoperative period one technique to decrease the risk of seroma collections and prevent implant migration is the use of perfusion holes. There are holes placed through the implant during surgery which will permit tissue ingrowth through them. It is a technique that creates partial tissue integration to the implant.
Pelvic Plasty
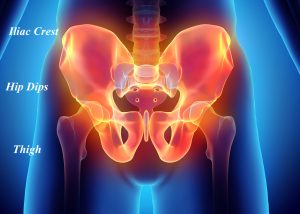
A unique form of hip augmentation is known as Pelvic Plasty. The hip region is bordered superiorly at the iliac crest and extends inferiorly down over the greater trochanter of the femur into the upper thigh. It can be divided into 3 zones based on what the patient wants to have augmented. Traditional hip implants augment either the hip dip area between the iliac crest and the greater trochanter (Zone 2) or both Zone 2 and the area below into the upper thigh. (Zone 3)
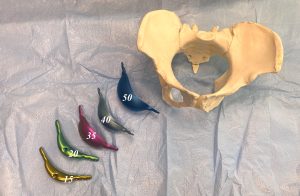
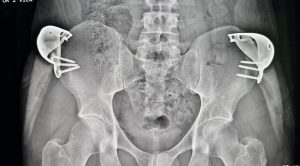
 Increasing pelvic bone width or Zone 1 hip enhancement has never previously been augmented because there has never been a method to do so. Zone 1 augmentation requires increasing pelvic width by adding to the wing of the ilium with an implant attached to the iliac crest. This is now capable of being done by a special designed titanium iliac crest implant that is fixed to the bone by screws. It is available in multiple widths of 15 to 50mms. It is placed through a small incisi0n just below the anterior superior iliac spine.
Increasing pelvic bone width or Zone 1 hip enhancement has never previously been augmented because there has never been a method to do so. Zone 1 augmentation requires increasing pelvic width by adding to the wing of the ilium with an implant attached to the iliac crest. This is now capable of being done by a special designed titanium iliac crest implant that is fixed to the bone by screws. It is available in multiple widths of 15 to 50mms. It is placed through a small incisi0n just below the anterior superior iliac spine.

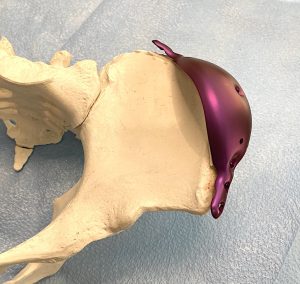
 Increasing pelvic bone width can often make the subiliac hip dip area deeper or more indented. For this reason many patients benefit by the simultaneous placement of a silicone hip dip implant that is designed to fit or hook into the underside of the titanium iliac crest plate.
Increasing pelvic bone width can often make the subiliac hip dip area deeper or more indented. For this reason many patients benefit by the simultaneous placement of a silicone hip dip implant that is designed to fit or hook into the underside of the titanium iliac crest plate.
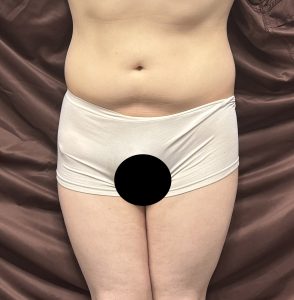
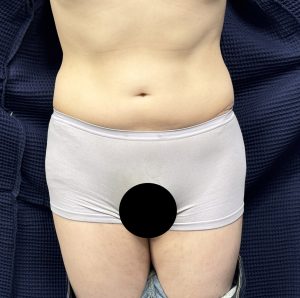 There are two types of patients that may seek the Pelvic Plasty procedure. One is the cis-female who has a straight body profile with no curves or the transfemale who naturally has genetically more narrow hips and would benefit from wider pelvic appearance.
There are two types of patients that may seek the Pelvic Plasty procedure. One is the cis-female who has a straight body profile with no curves or the transfemale who naturally has genetically more narrow hips and would benefit from wider pelvic appearance.
THIGH IMPLANTS
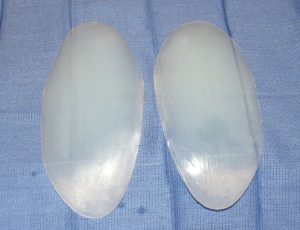 Enhancing the upper thigh of the leg is done by augmentation of the single largest muscle belly on the anterior thigh, the rectus femoris. Its long length and reasonable width provide a subfascial tissue pocket for a sizaboe implant. Since there are no standard thigh implants available, these are made custom for each patient.
Enhancing the upper thigh of the leg is done by augmentation of the single largest muscle belly on the anterior thigh, the rectus femoris. Its long length and reasonable width provide a subfascial tissue pocket for a sizaboe implant. Since there are no standard thigh implants available, these are made custom for each patient.
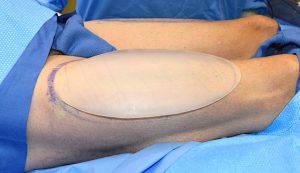
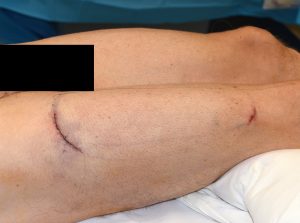 Thigh implants are done in the supine position in surgery through a curved upper lateral thigh skin incision. This provides immediate access to the muscle fascia under which the implants are placed. In some cases a small low thigh incision is made to ensure that the implant’s position on top of the muscle.
Thigh implants are done in the supine position in surgery through a curved upper lateral thigh skin incision. This provides immediate access to the muscle fascia under which the implants are placed. In some cases a small low thigh incision is made to ensure that the implant’s position on top of the muscle.
CALF IMPLANTS
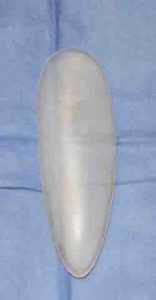 Creating fullness in the lower leg can help both men and women who have very skinny legs or ‘chicken legs’ due to natural underdevelopment and an inability to increase calf size by exercise. There are also some people born with clubfoot who have disproportionately small calf muscles. Calf implants have an elongated shape that are available in different lengths, widths and thickness. Calf implants may be used to build up the inside of the leg (medial head gastrocnemius muscle) or combined with outside of the calf (lateral head gastrocnemius muscle) as well.
Creating fullness in the lower leg can help both men and women who have very skinny legs or ‘chicken legs’ due to natural underdevelopment and an inability to increase calf size by exercise. There are also some people born with clubfoot who have disproportionately small calf muscles. Calf implants have an elongated shape that are available in different lengths, widths and thickness. Calf implants may be used to build up the inside of the leg (medial head gastrocnemius muscle) or combined with outside of the calf (lateral head gastrocnemius muscle) as well.
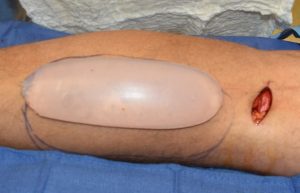 Calf implants are placed through small incisions on the back of the knee. Different incision locations are used on the back of the knee depending upon which head of the calf muscle is being augmented. Calf implants are placed on top of the muscle in the subfascial location. To properly perform the surgery the patient is placed in the prone position during surgery.
Calf implants are placed through small incisions on the back of the knee. Different incision locations are used on the back of the knee depending upon which head of the calf muscle is being augmented. Calf implants are placed on top of the muscle in the subfascial location. To properly perform the surgery the patient is placed in the prone position during surgery.
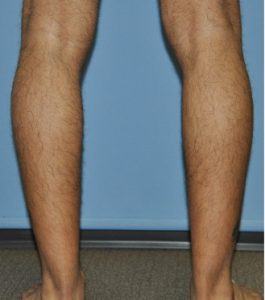
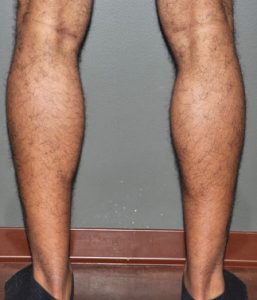 Calf implants can be used to build up just the inner or outer gastrocnemius muscle or both depend upon the effect the patient desires. A part of the inner muscle can also be built below the inner knee in women who had a later concave shape in that area.
Calf implants can be used to build up just the inner or outer gastrocnemius muscle or both depend upon the effect the patient desires. A part of the inner muscle can also be built below the inner knee in women who had a later concave shape in that area.
TESTICLE IMPLANTS
 The one type of male body implant that is not a muscle enhancer is that of scrotal augmentation by the placement of testicle implants. Testicle implants have been around for decades and have been most commonly used for replacement of a missing or lost testicle. Their uses today have been expanded for aesthetic augmentations as well.
The one type of male body implant that is not a muscle enhancer is that of scrotal augmentation by the placement of testicle implants. Testicle implants have been around for decades and have been most commonly used for replacement of a missing or lost testicle. Their uses today have been expanded for aesthetic augmentations as well.
![]() The most common testicle implant is a saline-filled device. But this does not have the feel of a natural testicle as a fluid-filled implant is very hard, has limited size options that are often too small, and will eventually deflate and need to be replaced. I only use an ultrasoft solid silicone implant that feels much more natural, will never fail or need to be replaced and the size options are virtually unlimited because of the custom design process for any size 6.0cms or greater.
The most common testicle implant is a saline-filled device. But this does not have the feel of a natural testicle as a fluid-filled implant is very hard, has limited size options that are often too small, and will eventually deflate and need to be replaced. I only use an ultrasoft solid silicone implant that feels much more natural, will never fail or need to be replaced and the size options are virtually unlimited because of the custom design process for any size 6.0cms or greater.
Custom Testicle Implants Placement Dr Barry Eppley IndianapolisSuch ultrasoft solid silicone testicle implants are often made custom for each patient and are introduced through a midline raphe skin incision.
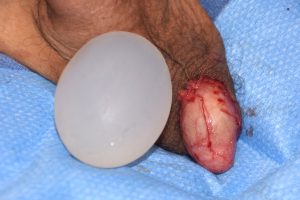
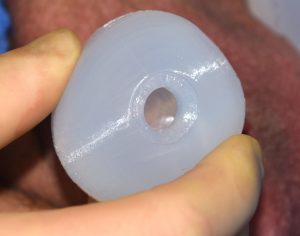 Besides the replacement of a missing testicle or of an existing saline testicle implant, silicone testicle implants can be used for aesthetic enlargement even with existing natural testicles in place. There are two implant approaches to do so, a side by side technique (if one’s existing testicles are small enough) or a wrap around or clamshell style of testicle enlargement implant. In this custom testicle implant design, the existing testicle fits inside the implant with an exit for the spermatic and neuromuscular cord. There are advantages and disadvantages with either approach but most older men usually opt for the side by side technique as their natural testicles have usually undergone some degree of atrophy.
Besides the replacement of a missing testicle or of an existing saline testicle implant, silicone testicle implants can be used for aesthetic enlargement even with existing natural testicles in place. There are two implant approaches to do so, a side by side technique (if one’s existing testicles are small enough) or a wrap around or clamshell style of testicle enlargement implant. In this custom testicle implant design, the existing testicle fits inside the implant with an exit for the spermatic and neuromuscular cord. There are advantages and disadvantages with either approach but most older men usually opt for the side by side technique as their natural testicles have usually undergone some degree of atrophy.
CUSTOM BODY IMPLANTS
While a diverse number of preformed styles and sizes are available in the different body implants, they may not be adequate for all patient’s aesthetic needs. This could be due to size (volume) or shape of the preformed implants. (e.g., desire for very large pectoral or buttock implants) It could also be for a body augmentation site for which implants are not currently made (e.g., hip and thigh implants) or for a unique reconstructive body defect. (e.g., pectus excavatum, Poland’s syndrome)
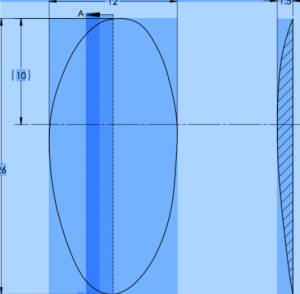 This is where the role of custom designing of body implants for a specific patient need has great value. Custom body implants can be made by four different methods. First, if the desired custom implant is close to a preformed one and only differs by a known dimensional amount the preformed implant computer design file can be be changed and the desired implant 3D printed. Second, direct measurements can be taken on the patient and converted into a computer design file for implant fabrication.
This is where the role of custom designing of body implants for a specific patient need has great value. Custom body implants can be made by four different methods. First, if the desired custom implant is close to a preformed one and only differs by a known dimensional amount the preformed implant computer design file can be be changed and the desired implant 3D printed. Second, direct measurements can be taken on the patient and converted into a computer design file for implant fabrication.

 The third custom implant design method is a moulage or impression of the body defect site made from an elastic polymer done on the patient. The moulage elastomers are mixed together, molded into the desired implant shape and size on the patient and allowed to Harden. It is then sent to the manufacturer to be scanned and converted into a computer design file. Lastly, and the most infrequently done method, is that a custom body implants can be designed from a 3D CT scan of the patient.
The third custom implant design method is a moulage or impression of the body defect site made from an elastic polymer done on the patient. The moulage elastomers are mixed together, molded into the desired implant shape and size on the patient and allowed to Harden. It is then sent to the manufacturer to be scanned and converted into a computer design file. Lastly, and the most infrequently done method, is that a custom body implants can be designed from a 3D CT scan of the patient.
 Regardless of the design method used, the typical turnaround time to have custom body implants made and ready for surgery is four to six weeks. The most common custom body implants in my experience are hip and testicle implants as well as sternal and chest wall implants for congenital defects.
Regardless of the design method used, the typical turnaround time to have custom body implants made and ready for surgery is four to six weeks. The most common custom body implants in my experience are hip and testicle implants as well as sternal and chest wall implants for congenital defects.
Body Implants – Before Surgery
An examination and measurements are taken of the body area to be augmented. It is important to match the area of implantation with the size of the implants to avoid an augmentation that is aesthetically too small or one in which deformity occurs afterward because it is too big for the pocket. Patients need to be aware of the risk and complications which include scarring, infection, implant asymmetry and displacement, aesthetic dissatisfaction and the risk of the need for revisional surgery. Collectively, body implants have an average revision/complication risk of 10% to 15%.
Body Implants – Operation
All body implants require incisions to be placed and these must be carefully considered in the aesthetics of the procedure. Body implants always perform best (better vascularized tissue cover) when placed into or under muscle but that is only possible for pectoral and buttock implants. All other body implants are placed in the subfascial location. (above the muscle) All body implants are done under general anesthesia as an outpatient procedure.
Cosmetic Procedures – Body Implants – After Surgery
Dissolvable sutures are used for all body implant incisions. The augmented area(s) will have a garment/compression wrap on it to help control swelling and make moving around more comfortable. It will usually take 2 to 3 weeks after surgery until one feels comfortable doing all normal activities of daily. Exercise of any significance (running, lifting weights, Pilates, etc.) should not be done until about 3 week after surgery and may be longer for some types of body implants.

North Meridian Medical Building
Address:
12188-A North Meridian St.
Suite 310
Carmel, IN 46032
Contact Us:
Phone: (317) 706-4444
WhatsApp: (317) 941-8237
